What Are Integrated Labels?

Integrated labels, sometimes known as ‘integral labels’, ‘peel-out labels’ or ‘shipping labels’ are a paper-based document, usually A4 in size, with adhesive labels incorporated into it. This simple label and paper combination can save order processing time and improve order accuracy, as well as labour efficiency. Integrated labels are used to combine various documentation onto one single sheet, which can reduce the time it takes to print the documents and it removes the need to purchase both the sheets of labels and the paper.
Integrated labels usually come in single, double and triple. This is one, two or three integrated labels per sheet including adhesive to suit any application. Many companies are starting to use these labels for their daily operations due to the many benefits when using them, and they can be used to streamline the shipping process as they are able to combine shipping labels and your customers’ invoices.

What are integrated labels used for?
Integrated labels are mostly used for the delivery of products or services, and companies that utilise these labels have significantly improved efficiency within their operations by printing multiple pieces of information onto one sheet, such as the order information or invoice with the delivery/returns labels.
Integrated labels are also often used for:
- Return Labels: Integrated labels simplify the process of creating return labels for customers.
- Dispatch Labels: They are used for printing dispatch labels along with order details.
- Invoice Labels: These labels include both the invoice and the shipping label on the same sheet.
- Shipping Documents: Integrated labels combine shipping labels with important shipping documents.
- Packing Slips: They provide a packing slip with a built-in label for easy attachment.
- Delivery Notes: These labels include delivery notes and a corresponding label.
- Bullet Labels: Integrated labels can be used to print bullet labels for various purposes.
- Pharmaceutical Labels: They are used for creating pharmaceutical labels with relevant information.
- Information Labels: Integrated labels combine information labels with additional documentation.
The benefits of integrated labels
Integrated labels can be completely personalised with any laser or inkjet printer, making your delivery or dispatch notes fit in with your brand identity. These can be done at the same time as the return or address labels, which greatly reduces errors, time and money spent. Making major improvements in efficiency when using integrated labels allows for more time to increase productivity in the workplace. More benefits of integrated labels include:
-
Completely Personalised and Customisable: Integrated labels can be tailored to fit specific needs, allowing businesses to design the layout, size, and content according to their requirements. This customisation ensures that all necessary information is included, and branding is consistent.
-
Easy and Hassle-Free to Use: With integrated labels, the process of printing and labelling becomes straightforward. There’s no need to match separate labels to documents, reducing the steps and effort involved in preparing shipments or products.
-
Reduced Errors: By printing both the label and the associated information (such as invoices or packing slips) on the same sheet, the risk of mismatched or incorrect labelling is significantly lowered. This integrated approach helps ensure accuracy in shipping and product handling.
-
Efficient – Save Time and Money: Integrated labels streamline the workflow by combining multiple tasks into one. This efficiency reduces the time spent on printing and applying labels separately. Additionally, it cuts down on the cost of purchasing separate labels and sheets, leading to overall savings in operational expenses.
Easy returns make consumers happy!
Integrated labels help keep all of the documentation of an order in one specific place, which can greatly reduce the risk of errors in shipping. However, if a customer does require a return on an item, using integrated labels will save your company a lot of time processing the return due to the label being included in the order. This makes for an easier return for both you and the consumer, as well as providing excellent customer service, which can increase consumer loyalty.
How To Use Integrated Labels
- Integrated labels are usually designed to match an existing layout from a popular software or e-commerce platform, such as Amazon Marketplace. Therefore, this will need to be taken into consideration when choosing the label best matched to your desired platform or software.
- It is recommended that you should try a test print after you choose the integrated label that is most suited to your company and needs. This is the safest option before printing orders in bulk.
- It is important that all the information on the labels is aligned with your choice of integrated label, so checking the paper size and making sure the configurations match the label dimensions is the third key step. This is crucial since you want to ensure consistent results.
- Margins are also important; you want to be able to have a header, footer and left and right margins. This part may be trial and error, but we can of course make sure it is suitable to your needs.
- Once the labels are perfect, we can save your preferences for future orders which will save time and allow an efficient operation process.
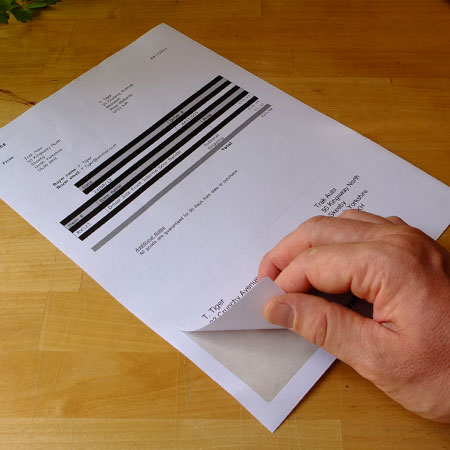

Which Label?
You are able to choose from 25 formats with Labels Zoo to suit your software or e-commerce solutions. Different sites are able to work with our labels, such as: Amazon Marketplace, Paypal Packing Slips, eBay Selling Manager Pro, Actinic, Sage, Quickbooks plus many more! If you’d like more information, feel free to visit our Integrated Labels page.
Need more information?
At Labels Zoo, we are able to produce a huge variety of labels for our clients across a wide range of industries. Our Zoo Keepers are market leading experts when it comes to labels, and they will be happy to help and guide you through the process and any questions you may have. Don’t hesitate, we’re here to help!